Outdoor schools of various kinds are becoming increasingly popular. They are a good way of making children aware of the environment as a whole and their part in it and also afford opportunities for healthy exercise.
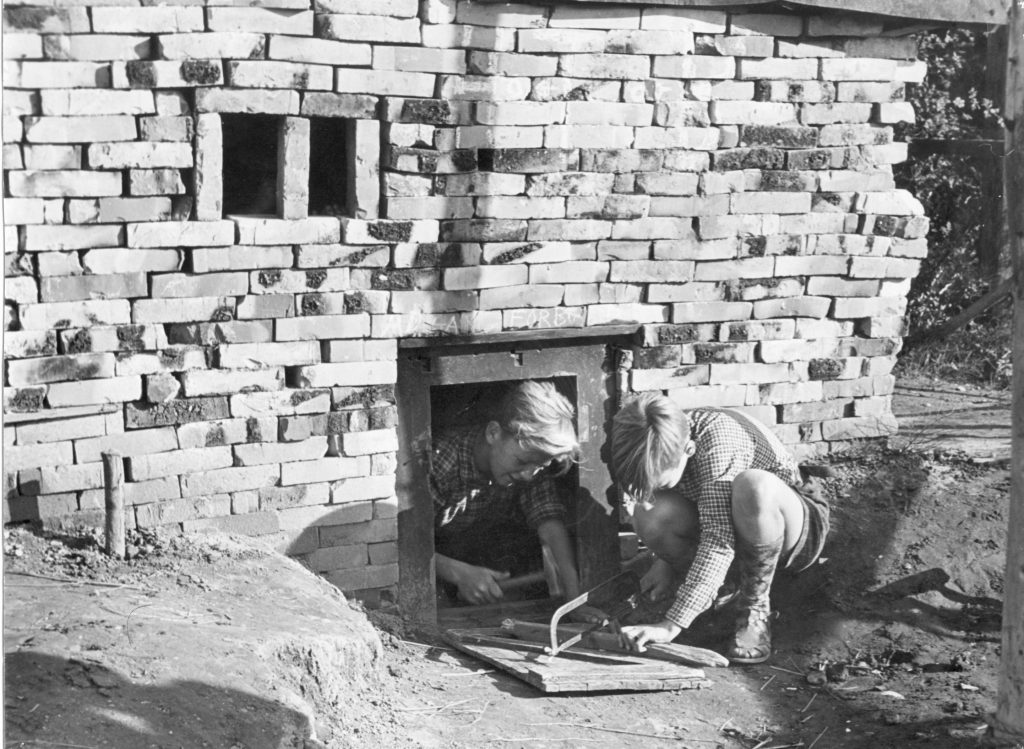
Although its origins can be traced back to the 19th century, the modern outdoor school seems to have originated in Scandinavia. In addition, Denmark also has the distinction of inventing the ‘junk playground’ (skrammellegepladsen). The first one of these was founded in Emdrup in 1943 during the dark days of the German Occupation of Denmark.
John Bertelsen, who ran it, had been trained at a teacher training college where a free and anti-authoritarian atmosphere prevailed. Radical ideas and new thinking were encouraged, as was a critical view of capitalism: “Mankind is good, but his development is hampered by the culture of the bourgeois society.” Many of the students looked forward to a future socialist utopia. It is perhaps not surprising that Bertelsen spent three months in prison for Resistance activities.
Developing through play
In the 1930s, cultural radicals advocating for reformist ideas in pedagogy were questioning the prevailing wisdom that it was necessary for adults to force knowledge into children. Rather, they contended, the children themselves should be allowed to develop naturally – and this included using play. These ideas can be traced back to those of the 18th century philosopher Jean-Jacques Rousseau, who formulated the concept of the ‘natural human’.
Ole Schultze Henriksen, an academic who worked in junk playgrounds for 20 years and who has written a history of them, says that the ideas behind them were formed by the landscape architect Carl Theodor Sørensen.
“He thought that children didn’t need conventional play furniture such as climbing frames or slides; they should just be given earth, pieces of wood, bricks and shovels,” Henriksen told CPH POST.
Sørensen’s goal, continued Henriksen, was to create a place where children were able to be creative and play where “they can dream and fantasise and make their dreams and fantasies real”. Sørensen wanted to give urban children the same possibilities as those enjoyed by children growing up in the country.
This, of course, is very much in tune with the ideas of Friedrich Froebel, the creator of the kindergarten, which literally means ‘children’s garden’. Moreover, ‘kindergarten’ signifies both a garden for children as a location where they can observe and interact with nature, but also a garden of children, where they themselves can grow and develop in freedom from arbitrary imperatives.
Outdoor schools today
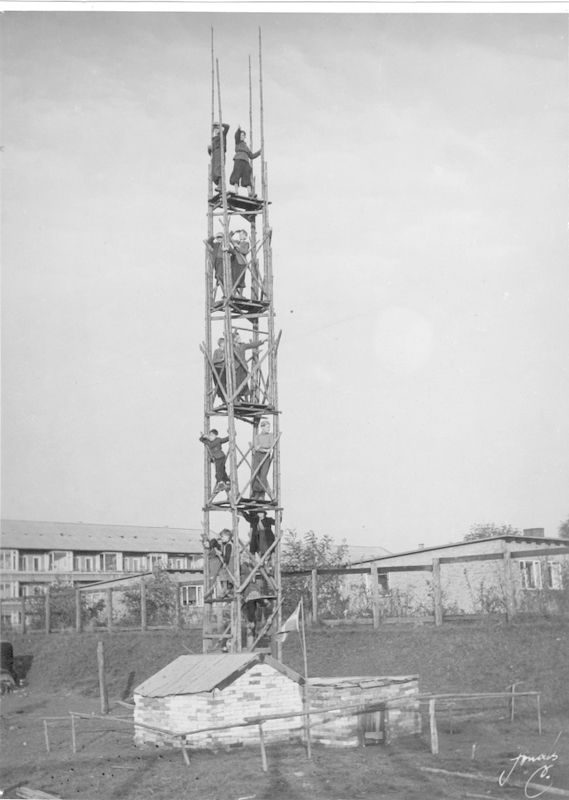
Junk playgrounds in the form in which they were originally conceived have more or less ceased to exist. Many of them have been demolished and the remaining ones are now under the auspices of after-school clubs.
“In my opinion, the playgrounds have lost the originality, strength and idealism that they once had, so today, it is difficult to distinguish them from ‘normal’ children’s day institutions,” contended Henriksen.
However, some of the ideas of the educational reformers from the past do live on, and outdoor schools embrace some of that spirit of adventure and ‘hands on’ teaching methods designed to reconnect children with nature and the natural world.
‘Outdoor school’ or ‘nature school’ is a broad term that describes regular teaching taking place in nature or in cultural surroundings. This can mean in woods, parks, in the local community, firms, museums and on farms. It is an extension and supplement to normal schooling activities and is characterised by teachers making use of the local environment when teaching specific subjects and curriculum areas. For example, natural objects can be incorporated into projects in mathematics or literature and visits to culturally important sites bring history lessons to life.
According to Niels Ejbye-Ernst, a researcher at the University of Copenhagen, the first record of a Danish outdoor school is from 1950, when Ella Flatau started a ‘walking kindergarten’ that included a daily hike in the woods as part of the curriculum. Within a few years, mothers began organising schools that transported their children from Copenhagen’s congested neighbourhoods into the countryside.
The concept has now been extended to older children, as more and more schools have started introducing curriculum-based outdoor learning as a weekly or fortnightly ‘outdoor school’ day for children aged 7-16.
Do they work?
Case studies have shown that teaching across multiple platforms can foster better relations between children and between children and teachers in a class.
Experienced outdoor-school teachers all emphasise that the system is very good at motivating children. Most of them point out that the variation offered by outdoor schools contributes to a large number of children actually enjoying going to school. They also say that children become more actively communicative when they are at an outdoor school.
What do the kids think?
In 2015, a survey was carried out to ascertain what the children who attended outdoor schools thought of them. The survey gathered data from 689 children from seven schools throughout Denmark. The vast majority of children who were asked completed the survey.
The survey concluded that Danish children are positive about outdoor schools. Some 77 percent of the children agreed with the precept ‘I like tuition when we have outdoor school’ and 68 percent agreed that ‘I look forward to outdoor school’.
It was not only age-specific, as both young and older children said they enjoyed outdoor school. However, the survey did show (perhaps unsurprisingly) that boys enjoy outdoor school more than girls, although both sexes enjoy the learning process at an outdoor school. The boys also found it easier to concentrate on teaching and to remember what they’ve learnt.
So maybe Rousseu et al were really on to something, and the concept has a future after all?