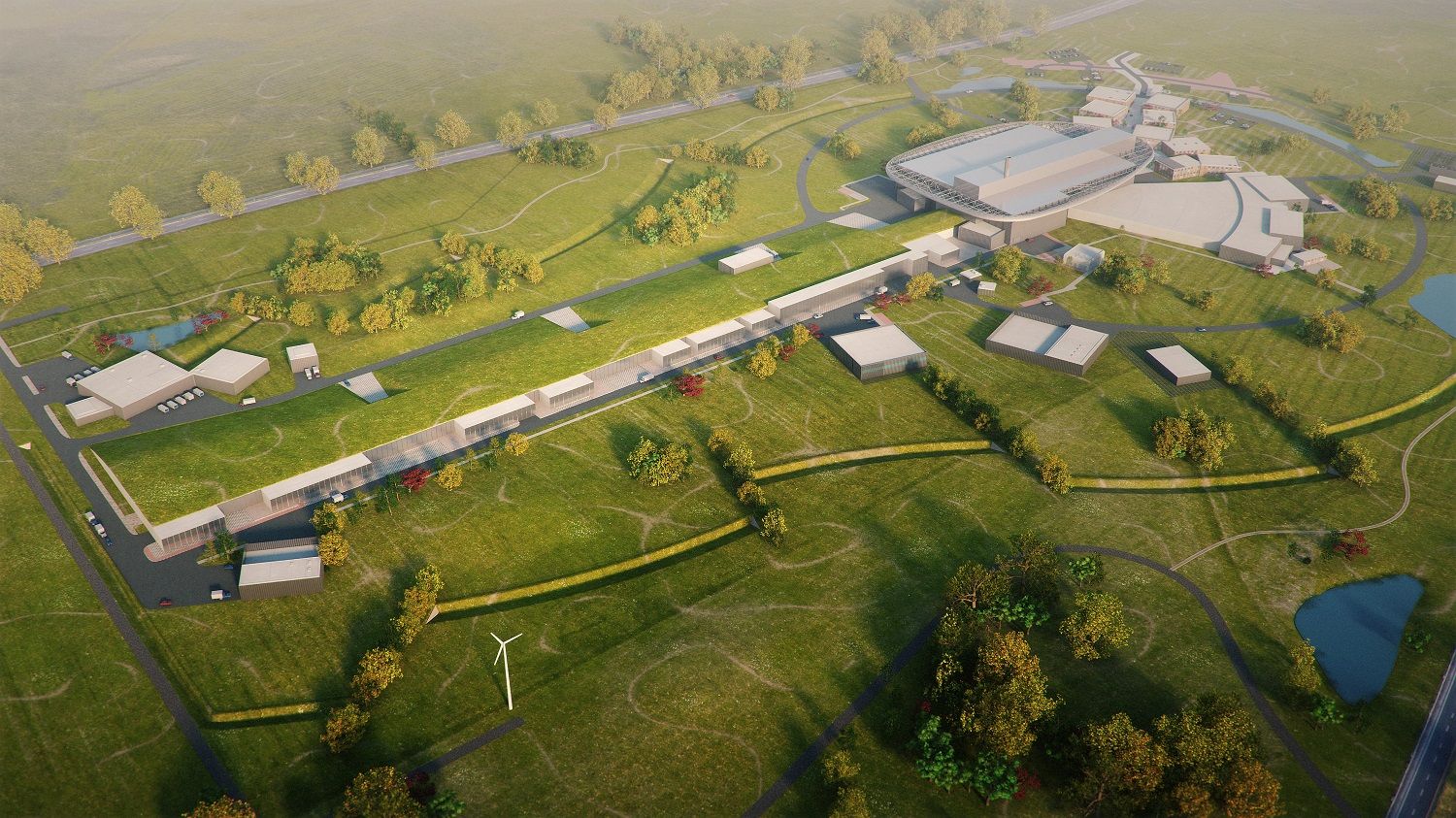
The European Commission has officially adopted the European Spallation Source (ESS) – which until now has been co-hosted by Sweden and Denmark – as a European Research Infrastructure Consortium.
The massive science research facility, which uses the neutron scattering technique, will in future also be co-owned by the Czech Republic, France, Germany, Hungary, Italy, Norway, Poland, Estonia and Switzerland.
“We are proud and thankful that ESS will be supported by so many European countries,” said the education and research minister, Esben Lunde Larsen.
“It provides ESS the best conditions to develop into a European research centre that will be world-class and where talented researchers from all over the world can congregate to undertake groundbreaking experiments.”
READ MORE: Construction begins on world’s most advanced neutron research centre
European research hub
For now, the UK, Belgium and Spain will take part in ESS meetings as observers, but the three nations are expected to become co-owners as well in the not too distant future.
Denmark will continue to be a central driving capacity regarding the development of ESS and will take part in the development and construction of the main centre, which will be located in Lund, Sweden. A data centre will also be established at the Nørre Campus in Copenhagen.
The massive science research facility, which is the world’s most advanced neutron microscope, is expected to have 400-500 full-time employees and welcome 2,000-5,000 visiting researchers every year. It is expected to be ready for use in 2019, while the research centre is scheduled to be completed by 2025.